|
|---|
これは日々の作業を通して学んだことや毎日の生活で気づいたことをを記録しておく備忘録である。
HTML ファイル生成日時: 2026/03/04 08:17:24.833 (台灣標準時)
Astropy の astropy.modeling を使って最小二乗法によるフィッティングを行 う方法を調べてみたでござる。その方法を記録しておくでござる。
まず、以下のプログラムで、フィッティングを行うデータを生成するでござる。
#!/usr/pkg/bin/python3.13 # # Time-stamp: <2025/04/03 21:58:58 (UT+08:00) daisuke> # # importing numpy import numpy # output file name file_output = 'synthetic_00.data' # parameters x_min = 0.0 x_max = 50.0 n_data = 30 a = 2.0 b = 3.0 # random number generator rng = numpy.random.default_rng () # function y=a*x+b def func (a, b, x): y = a * x + b return (y) # generation of data data_x = rng.uniform (x_min, x_max, n_data) data_y = func (a, b, data_x) + rng.normal (loc=0.0, scale=0.5, size=n_data) data = numpy.array ([data_x, data_y]).T # writing data to file with open (file_output, 'w') as fh_w: for (x, y) in data: fh_w.write (f'{x:7.3f} {y:7.3f}\n')
上のプログラムを実行してみるでござる。
% python3.13 fitting_astropy_00_generate_data.py % head synthetic_00.data 4.402 12.373 45.926 95.514 10.593 24.500 42.116 88.686 38.252 80.420 3.602 10.026 28.959 60.545 25.399 53.605 40.849 84.548 39.854 82.616
最小二乗法によるフィッティングを行うためには、例えば、以下のようなプロ グラムを用意すればよいようでござる。
#!/usr/pkg/bin/python3.13 # # Time-stamp: <2025/04/03 22:02:55 (UT+08:00) daisuke> # # importing numpy module import numpy # importing astropy module import astropy.modeling # importing matplotlib module import matplotlib.backends.backend_agg import matplotlib.figure # input file name file_input = 'synthetic_00.data' # output file name file_output = 'fitting_00.png' # making empty lists for storing data list_x = [] list_y = [] # opening data file with open (file_input, 'r') as fh_r: # reading data file line-by-line for line in fh_r: # skipping if line starts with '#' if (line[0] == '#'): continue # splitting line (x_str, y_str) = line.split () # converting string into float try: x = float (x_str) except: continue try: y = float (y_str) except: continue # appending data to lists list_x.append (x) list_y.append (y) # making numpy arrays array_x = numpy.array (list_x) array_y = numpy.array (list_y) # initialisation of fitter fitter = astropy.modeling.fitting.LevMarLSQFitter (calc_uncertainties=True) # model used for fitting model_linear = astropy.modeling.models.Linear1D () # carrying out a fitting fitted_func = fitter (model_linear, array_x, array_y) # degree of freedom dof = len (array_x) - 2 print (f'dof = {dof}') # calculation of reduced chi square chi_square = sum ( (fitted_func (array_x) - array_y)**2 ) reduced_chi_square = chi_square / dof print (f'chi square = {chi_square}') print (f'reduced chi square = {reduced_chi_square}') # fitted parameters a = fitted_func.slope.value b = fitted_func.intercept.value a_err = (fitter.fit_info['param_cov'][0,0])**0.5 b_err = (fitter.fit_info['param_cov'][1,1])**0.5 print (f'a = {a:8.5f} +/- {a_err:8.5f}') print (f'b = {b:8.5f} +/- {b_err:8.5f}') # making a fig object using object-oriented interface fig = matplotlib.figure.Figure () # making a canvas object canvas = matplotlib.backends.backend_agg.FigureCanvasAgg (fig) # making an axes object ax = fig.add_subplot (111) # plotting data ax.plot (array_x, array_y, \ linestyle='None', marker='o', markersize=3, color='blue', \ label='synthetic data points') # plotting fitted line fitted_x = numpy.linspace (0.0, 50.0, 10000) fitted_y = fitted_func (fitted_x) ax.plot (fitted_x, fitted_y, \ linestyle=':', color='red', linewidth=2, \ label='fitted line') # axes ax.legend () ax.grid () ax.set_xlabel ('X [arbitrary unit]') ax.set_ylabel ('Y [arbitrary unit]') # saving plot into file fig.savefig (file_output, dpi=225)
上のプログラムを実行してみるでござる。
% python3.13 fitting_astropy_01_leastsquares.py WARNING: Model is linear in parameters; consider using linear fitting methods. [astropy.modeling.fitting] dof = 28 chi square = 6.482639200079887 reduced chi square = 0.23152282857428166 a = 2.01095 +/- 0.00554 b = 2.89295 +/- 0.17692
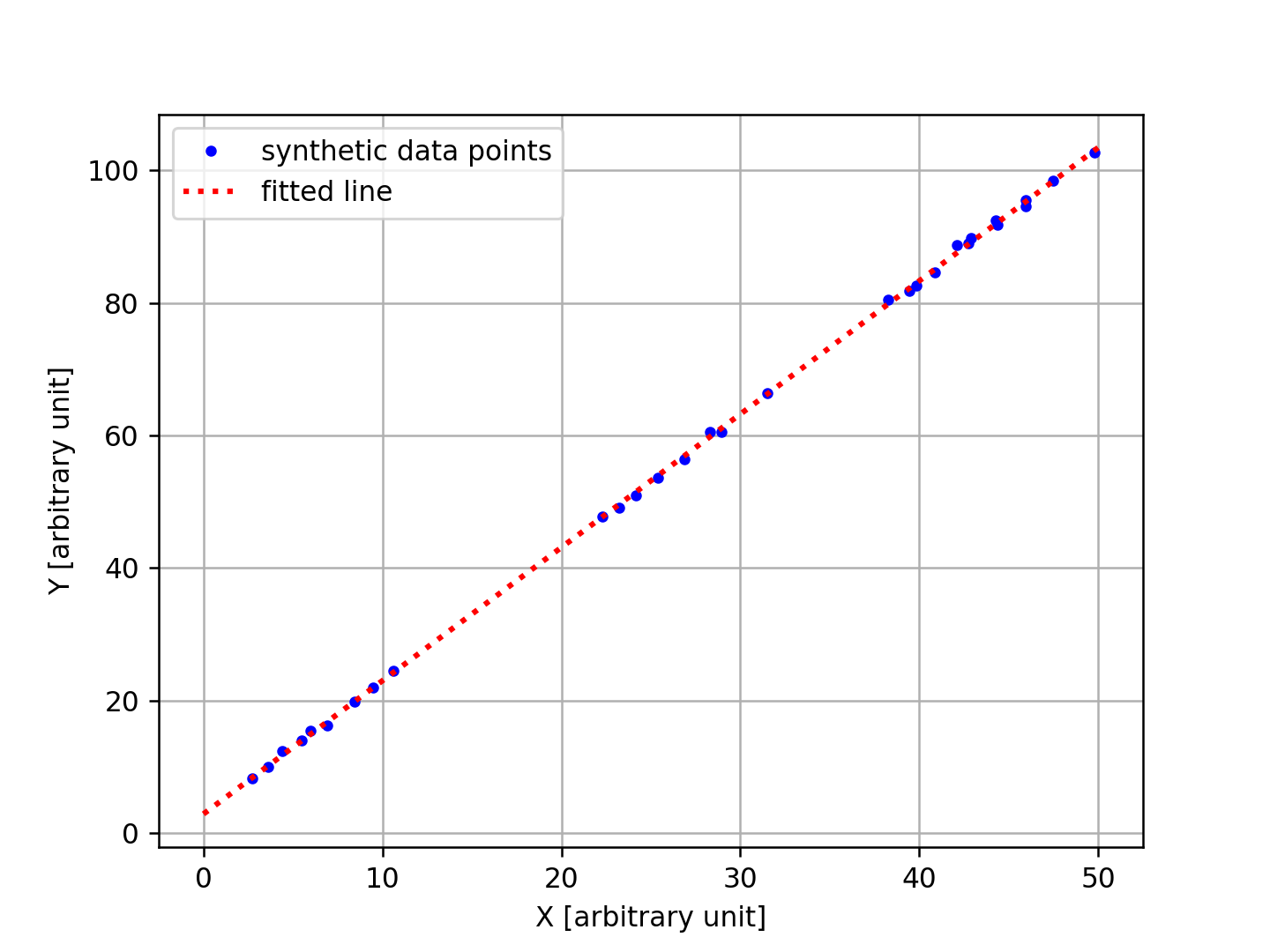
作成された図は以下の通りでござる。

|
|---|
gnuplot でも、フィッティングを行ってみて、結果を比べてみるでござる。
% gnuplot G N U P L O T Version 6.0 patchlevel 1 last modified 2024-05-13 Copyright (C) 1986-1993, 1998, 2004, 2007-2024 Thomas Williams, Colin Kelley and many others gnuplot home: http://www.gnuplot.info faq, bugs, etc: type "help FAQ" immediate help: type "help" (plot window: hit 'h') Terminal type is now x11 gnuplot> f(x) = a*x+b gnuplot> fit f(x) 'synthetic_00.data' using 1:2 via a,b iter chisq delta/lim lambda a b 0 3.4608242543e+04 0.00e+00 2.26e+01 1.000000e+00 1.000000e+00 1 4.0754622240e+01 -8.48e+07 2.26e+00 2.043468e+00 1.054945e+00 2 1.0656335996e+01 -2.82e+05 2.26e-01 2.031357e+00 2.141778e+00 3 6.4828360181e+00 -6.44e+04 2.26e-02 2.011091e+00 2.887789e+00 4 6.4826392001e+00 -3.04e+00 2.26e-03 2.010951e+00 2.892947e+00 5 6.4826392001e+00 -1.50e-08 2.26e-04 2.010951e+00 2.892948e+00 iter chisq delta/lim lambda a b After 5 iterations the fit converged. final sum of squares of residuals : 6.48264 rel. change during last iteration : -1.50162e-13 degrees of freedom (FIT_NDF) : 28 rms of residuals (FIT_STDFIT) = sqrt(WSSR/ndf) : 0.481168 variance of residuals (reduced chisquare) = WSSR/ndf : 0.231523 Final set of parameters Asymptotic Standard Error ======================= ========================== a = 2.01095 +/- 0.005536 (0.2753%) b = 2.89295 +/- 0.1769 (6.116%) correlation matrix of the fit parameters: a b a 1.000 b -0.868 1.000 gnuplot> exit
同じ結果が得られたでござる。